Page 295 - Teacher Preview Copy
P. 295
.
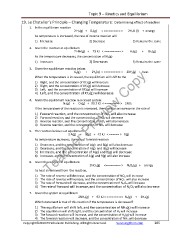
Topic 9 – Kinetics and Equilibrium
19. Le Chatelier’s Principle – Changing Temperature: Determining effect of reaction
1. In the equilibrium reaction 2 H2(g) + O2(g) < ========== > 2H2O (l) + energy
As temperature is increased, the rate of reverse reaction will
1) Increase 2) Decrease 3) Remains the same
2. Given the reaction at equilibrium
2 HBr(g) + 73 KJ < ========== > H2(g) + Br2(g)
As the temperature decreases, the concentration of H2(g)
1) Increases 2) Decreases 3) Remains the same
3. Given the equilibrium reaction below:
Teacher Preview Copy
Teacher Preview Copy
X2(g) + 2Y2(q) < ========== > 2XY2(g) + heat
When the temperature is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the
1) Right, and the concentration of XY2(g) will increase
2) Right, and the concentration of XY2(g) will decrease
3) Left, and the concentration of XY2(g) will increase
4) Left, and the concentration of XY2(g) will decrease
4. Given the equilibrium reaction in a closed system:
N2(g) + O2(g) + 90.7 KJ < ========= > 2NO2
If the temperature of the reaction is increased, there will be an increase in the rate of
1) Forward reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
2) Forward reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will decrease
3) Reverse reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
4) Reverse reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will decrease
5. The reaction below is at equilibrium
2 A(g) + B(g) + 42 KJ < ====== > C(g)
As temperature increases, the rate of forward reaction
1) Decreases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will also decrease
2) Decreases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will increase
3) Increases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will decrease
4) Increases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will also increase
6. Given the reaction at equilibrium
2NO2(g) <========= > N2O4(g) + energy
As heat is removed from the reaction,
1) The rate of reverse will decrease, and the concentration of NO2 will increase
2) The rate of reverse will increase, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
3) The rate of forward will decrease, and the concentration of N2O4 will increase
4) The rate of forward will increase, and the concentration of N2O4 will also increase
7. Given the system at equilibrium
2NH3(g) + 92 KJ < =========> N2(g) + 3H2(g)
Which statement is true of this reaction if the temperature is decreased?
1) The equilibrium will shift left, and the concentration of NH3(g) will increase
2) The equilibrium will shift right, and the concentration of H2 will increase
3) The forward reaction will increase, and the concentration of H2(g) will increase
4) The forward reaction will decrease, and the concentration of NH3 will decrease
Copyright©2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. SurvivingChem.com 285
Topic 9 – Kinetics and Equilibrium
19. Le Chatelier’s Principle – Changing Temperature: Determining effect of reaction
1. In the equilibrium reaction 2 H2(g) + O2(g) < ========== > 2H2O (l) + energy
As temperature is increased, the rate of reverse reaction will
1) Increase 2) Decrease 3) Remains the same
2. Given the reaction at equilibrium
2 HBr(g) + 73 KJ < ========== > H2(g) + Br2(g)
As the temperature decreases, the concentration of H2(g)
1) Increases 2) Decreases 3) Remains the same
3. Given the equilibrium reaction below:
Teacher Preview Copy
Teacher Preview Copy
X2(g) + 2Y2(q) < ========== > 2XY2(g) + heat
When the temperature is increased, the equilibrium will shift to the
1) Right, and the concentration of XY2(g) will increase
2) Right, and the concentration of XY2(g) will decrease
3) Left, and the concentration of XY2(g) will increase
4) Left, and the concentration of XY2(g) will decrease
4. Given the equilibrium reaction in a closed system:
N2(g) + O2(g) + 90.7 KJ < ========= > 2NO2
If the temperature of the reaction is increased, there will be an increase in the rate of
1) Forward reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
2) Forward reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will decrease
3) Reverse reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
4) Reverse reaction, and the concentration of NO2 will decrease
5. The reaction below is at equilibrium
2 A(g) + B(g) + 42 KJ < ====== > C(g)
As temperature increases, the rate of forward reaction
1) Decreases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will also decrease
2) Decreases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will increase
3) Increases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will decrease
4) Increases, and the concentration of A(g) and B(g) will also increase
6. Given the reaction at equilibrium
2NO2(g) <========= > N2O4(g) + energy
As heat is removed from the reaction,
1) The rate of reverse will decrease, and the concentration of NO2 will increase
2) The rate of reverse will increase, and the concentration of NO2 will also increase
3) The rate of forward will decrease, and the concentration of N2O4 will increase
4) The rate of forward will increase, and the concentration of N2O4 will also increase
7. Given the system at equilibrium
2NH3(g) + 92 KJ < =========> N2(g) + 3H2(g)
Which statement is true of this reaction if the temperature is decreased?
1) The equilibrium will shift left, and the concentration of NH3(g) will increase
2) The equilibrium will shift right, and the concentration of H2 will increase
3) The forward reaction will increase, and the concentration of H2(g) will increase
4) The forward reaction will decrease, and the concentration of NH3 will decrease
Copyright©2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. SurvivingChem.com 285