Page 2 - 20140903 PC Rumen Fluke
P. 2
PAGE 2 Please refer to the disclaimer on the last page regarding informaton in this leafet.
Introducton
Rumen fukes are parasites of ruminants and occur worldwide. They have a snail intermediate host. The adult
parasites live in the rumen (stomach) and the immature larval forms live in the small intestne. Clinical disease is
primarily due to intestnal damage caused by massive numbers of larvae in the intestne. The adult worms are usually
not considered to cause disease in the rumen.
In recent years, the prevalence of rumen fuke in Ireland and the United Kingdom has increased. A few fatal cases
have been recorded by the regional veterinary laboratory service and veterinary surgeons in practce see occasional
cases of clinical disease.
Many catle have small numbers of adult rumen fuke in their stomachs and have rumen fuke eggs in their faeces.
Small numbers of adult parasites cause litle or no damage. It is important to distnguish between the mere presence
of rumen fuke in animals that are performing well and disease associated with rumen fuke.
This leafet will give you some background informaton on rumen fuke. Your veterinary surgeon will help you reach
a diagnosis and decide if a control programme for rumen fuke is required on your farm. Liver fuke and rumen fuke
can be found on the same farm so it is important to remember that liver fuke disease is always harmful and should
be given priority, whereas rumen fuke only rarely causes disease.
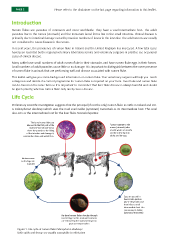
Life cycle
Preliminary scientfc investgaton suggests that the principal (if not the only) rumen fuke in catle in Ireland and U.K.
is Calicophoron daubneyi which uses the mud snail Galba (Lymnaea) truncatula as its intermediate host. This snail
also acts as the intermediate host for the liver fuke Fasciola hepatca.
The larval rumen fuke are
released in the frst part of the “Larvae migrate to the
small intestne (duodenum). rumen (stomach) afer
There they atach to the lining several weeks or months
of the intestne and damage it, and then develop into
causing diarrhoea and weight loss. adults and lay eggs
Metacercariae
on herbage are
ingested
Eggs are passed in
faeces onto pasture
where they hatch and
then infect a snail
intermediate host - the
commonest is Galba
(Lymnaea) truncatula.
The larval rumen fukes develop through
several stages in the snail untl cercariae
are released by the snail and encyst on
grass as metacercariae
Figure 1. Life cycle of rumen fuke Calicophoron daubneyi
Both catle and sheep are equally susceptble to infestaton
Figure 1. Life cycle of rumen fuke Calicophoron daubneyi
Both catle and sheep are equally susceptble to infestaton