Page 416 - Teacher Preview Copy
P. 416
Constructed Response . Topic 10: Organic Chemistry
Set J: Hydrocarbons, naming organic compounds, separation of mixture, diagram interpretation
Base your answers to questions 27 through 30 on the information and diagram below, and on your
knowledge of chemistry.
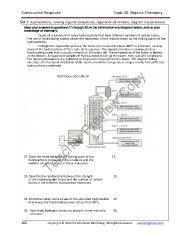
Crude oil is a mixture of many hydrocarbons that have different numbers of carbon atoms.
The use of fractionating towers allows the separation of this mixture bases on the boiling points of the
hydrocarbons.
o
To begin the separation process, the crude oil is heated to about 400 C in a furnace, causing
many of the hydrocarbons of the crude oil to vaporize. The vaporized mixture is pumped into a
fractionating tower that is usually more than 30 meters tall. The temperature of the tower is highest
at the bottom. As vaporized samples of hydrocarbons travel up the tower, they cool and condensed.
The liquid hydrocarbons are collected on trays and removed from the tower. The diagram below
illustrates the fractional distillation of the crude oil and the temperature ranges in which the different
hydrocarbons condensed.
Teacher Preview Copy
Distillation of Crude Oil
Teacher Preview Copy
27. State the trend between the boiling point of the 27.
hydrocarbons contained in the crude oil and the
number of carbon atoms in these molecules.
28. Describe the relationship between the strength 28.
of the intermolecular forces and the number of carbon
atoms in the different hydrocarbon molecules.
29. Write the IUPAC name of one of the saturated hydrocarbon 29.
o
that leaves the fractionating tower at less than 40 C.
30. How many hydrogen atoms are present in one molecule 30.
of octane.
406 Copyright © 2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. Survivingchem.com
Set J: Hydrocarbons, naming organic compounds, separation of mixture, diagram interpretation
Base your answers to questions 27 through 30 on the information and diagram below, and on your
knowledge of chemistry.
Crude oil is a mixture of many hydrocarbons that have different numbers of carbon atoms.
The use of fractionating towers allows the separation of this mixture bases on the boiling points of the
hydrocarbons.
o
To begin the separation process, the crude oil is heated to about 400 C in a furnace, causing
many of the hydrocarbons of the crude oil to vaporize. The vaporized mixture is pumped into a
fractionating tower that is usually more than 30 meters tall. The temperature of the tower is highest
at the bottom. As vaporized samples of hydrocarbons travel up the tower, they cool and condensed.
The liquid hydrocarbons are collected on trays and removed from the tower. The diagram below
illustrates the fractional distillation of the crude oil and the temperature ranges in which the different
hydrocarbons condensed.
Teacher Preview Copy
Distillation of Crude Oil
Teacher Preview Copy
27. State the trend between the boiling point of the 27.
hydrocarbons contained in the crude oil and the
number of carbon atoms in these molecules.
28. Describe the relationship between the strength 28.
of the intermolecular forces and the number of carbon
atoms in the different hydrocarbon molecules.
29. Write the IUPAC name of one of the saturated hydrocarbon 29.
o
that leaves the fractionating tower at less than 40 C.
30. How many hydrogen atoms are present in one molecule 30.
of octane.
406 Copyright © 2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. Survivingchem.com