Page 415 - Teacher Preview Copy
P. 415
Constructed Response . Topic 10: Organic Chemistry
Set H: Classes of organic compounds, organic reactions, relating molecular polarity to intermolecular forces
Base your answers to questions 22 through 24 on the information below.
The hydrocarbon 2–methylpropane reacts with iodine as represented by the balanced equation
below. At standard pressure,, the boiling point of 2–methylpropane is lower than the boiling
point of 2–iodo–2–methylpropane.
Teacher Preview Copy
Teacher Preview Copy
22. To which class of organic compound does this 22.
organic product belong?
23. Explain, in terms of bonding, why the hydrocarbon 23.
2-methylp ropane is saturated.
24. Explain the difference in the boiling points of 24. Molecular polarity:
2-methylpropane and 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
in terms of both molecular polarity and intermolecular
forces. Intermolecular forces:
Set I: Graph interpretation, relating intermolecular forces to boiling points
Base your answers to questions 25 and 26 on the information below.
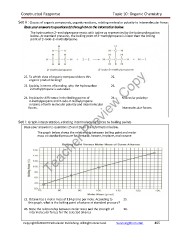
The graph below shows the relationship between boiling point and molar
mass at standard pressure for pentane, hexane, heptane, and nonane
25. Octane has a molar mass of 114 grams per mole. According to 25.
this graph, what is the boiling point of octane at standard pressure?
26. State the relationship between molar mass and the strength of 26.
intermolecular forces for the selected alkanes
Copyright©2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. SurvivingChem.com 405
Set H: Classes of organic compounds, organic reactions, relating molecular polarity to intermolecular forces
Base your answers to questions 22 through 24 on the information below.
The hydrocarbon 2–methylpropane reacts with iodine as represented by the balanced equation
below. At standard pressure,, the boiling point of 2–methylpropane is lower than the boiling
point of 2–iodo–2–methylpropane.
Teacher Preview Copy
Teacher Preview Copy
22. To which class of organic compound does this 22.
organic product belong?
23. Explain, in terms of bonding, why the hydrocarbon 23.
2-methylp ropane is saturated.
24. Explain the difference in the boiling points of 24. Molecular polarity:
2-methylpropane and 2-iodo-2-methylpropane
in terms of both molecular polarity and intermolecular
forces. Intermolecular forces:
Set I: Graph interpretation, relating intermolecular forces to boiling points
Base your answers to questions 25 and 26 on the information below.
The graph below shows the relationship between boiling point and molar
mass at standard pressure for pentane, hexane, heptane, and nonane
25. Octane has a molar mass of 114 grams per mole. According to 25.
this graph, what is the boiling point of octane at standard pressure?
26. State the relationship between molar mass and the strength of 26.
intermolecular forces for the selected alkanes
Copyright©2010 E3 Scholastic Publishing. All Rights Reserved. SurvivingChem.com 405